Inspection Order
The iQ-PAUF (Inspection Order Organization) component is a common system for any existing inspection orders. Where reasonable, it provides overall features for any type of inspection order. This ensures that the different inspections are handled in a unified manner even for very different types (such as for goods receipt inspection and management of measuring and test equipment) resulting in a quick acceptance by the users.
Workflow
The valid released inspection plan forms the basis for everything. It controls the processing of the inspection order by setting planned defaults. The inspection order can be created in different ways, for example, automatically when a new goods receipt is registered in the ERP system. After its creation, the order shall be processed what can happen at the appropriate inspection locations. During inspection, measurements or the result of a visual inspection can be entered supported by one-click confirmation buttons and failure catalogues. Finally, a usage decision is made and justified to initiate the follow-up activity. Inspection reports and evaluations complete the inspection order.
Important Features at a Glance
Inspection order types
- Initial sampling inspection
- Goods receipt inspection
- Reinspection orders for purchased parts
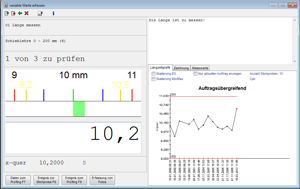 Inspection during production
Inspection during production
- Last part inspection
- Outgoing goods inspection
- Assembly inspection
- Laboratory inspection
- Inspections of measuring and test equipment
- Inspections during maintenance
Global features
The following paragraphs describe some important global features in note form.
Generating inspection orders
- Each type of inspection order supports different contents and defaults for inspection order creation.
- The inspection order creation procedure can be controlled by the user.
- Inspection orders can be automatically created on ERP systems.
- To create an order, it is normally necessary to use an inspection plan (see iQ-PLAN).
- Handling of deviations from the original design
- It is possible to record any important data belonging to an inspection order although this can be different for any order type. E. g., a goods receipt inspection would require data such as the article number, the supplier, quantities (target and actual), dates (target and actual date of shipping) or perhaps a charge number.
Changing and extending the inspection order content
- Changing target defaults, dates, quantities, efforts
- Reassignment of inspection location groups and inspection locations to other persons
- Changing characteristic specifications
- Adding new, unplanned characteristics
Controlling and monitoring inspection orders
- Assigning inspection procedures to inspection location (groups)
- Date monitoring
Performing inspection tasks
Despite the difference of the various inspection order types, there are some common functions:
- Overviews of inspection procedures
- Overviews of characteristics
- View of texts, drawings and images belonging to the inspection order or to any single characteristic
- Assessment of the inspection results on the characteristic level by using failure catalogues or specification limits
- Indication of the test equipment to be used
- Support of automatically taking over measurements from a connected measuring device
- Recording of additional data such as machine, tool, nest etc. for the different levels (inspection procedure, sample, or characteristic)
- Depending on the order type there are further specialized functions
Usage decisions (UD)
- Extensive analyzing options on the recorded history
- Characteristic level view of any inspection results
- Notes of the inspector
- Usage decisions for parts of deliveries
- Specification of the complaint
- Specification of the disposition under consideration of the ERP system
- Addition of annotations for inspection reports, supported by standard texts
- Inspection report generation in different languages
- Detailed recording of the inspection in the histories for supplier/part or cost center/part
- Usage decisions during production for single parts, partial lots, complete production
- Reporting of the usage decision back to the ERP
Deleting and cancelling inspection orders
Deleting or cancelling an inspection order is supported on an overview form that can be protected by permissions.
- The deletion would only erase the pure inspection order. Data that had been written to the supplier history would remain.
- Cancellation would remove the order including any derived calculations as if the order had never existed.
Evaluations
The module provides any evaluation that could be expected (too many for this summary) such as:
- Overviews
- Control charts
- Pareto diagrams
- Histograms
- Full qs-STAT (by Q-DAS) integration
Interfaces to Other Modules
