Prüfmittelfähigkeits-Untersuchung
Vor dem Einsatz eines Prüfmittels muss sichergestellt sein, ob die daran gestellten Anforderungen im robusten Dauerbetrieb erfüllt werden. Dafür werden Fähigkeitsuntersuchungen durchgeführt, die über die Kalibrierung deutlich hinausgehen. Es sind mögliche Schwachpunkte unter Berücksichtigung der Werksumgebung, der individuellen Benutzung durch Werker und des Dauerbetriebes durch Anwendung verschiedener Verfahren auszuschließen. In iQ-PMF sind die Anforderungen aus den Normen DIN EN ISO 9001, DIN EN ISO 10012, QS9000 und VDA 5 berücksichtigt worden. Der Entwicklung wurden die Verfahren der Schriftenreihe 10 (Fa. Bosch) zugrunde gelegt:
Verfahren 1: Ermittlung Streuung und Mittelwertslage der Messwerte
Verfahren 2: Bestimmung des Gesamtstreubereiches unter Einfluss von mehreren Bedienern
Verfahren 3: Bestimmung des Gesamtstreubereiches ohne Bedienereinfluss
Verfahren 4: Linearität
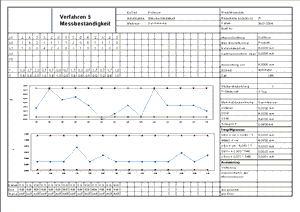
Verfahren 5: Messbeständigkeit/Stabilität
Verfahren 6: Prüfprozess für qualitative Merkmale
Workflow
Zu einer Fähigkeitsuntersuchung können mehrere Merkmale angelegt werden. Die Merkmalsdaten sind die Basis für alle zu diesem Merkmal durchzuführenden Verfahren. Für das Verfahren 2 und 3 ist das Verfahren 1 die Voraussetzung. Die Ergebnisse der Fähigkeitsuntersuchung werden dem einzelnen Prüfmittel zugeordnet. Das schlechteste Ergebnis aller Prüfmittel eines Typs wird dem Prüfmitteltyp zugewiesen. Damit kann man für eine vorgegebene Messaufgabe schnell das geeignete Prüfmittel herausfinden.
Wichtige Funktionen im Überblick
 Übersicht aller bisherigen Fähigkeitsuntersuchungen zu einem Prüfmitteltyp oder auch Prüfmittel
Übersicht aller bisherigen Fähigkeitsuntersuchungen zu einem Prüfmitteltyp oder auch Prüfmittel
- Je Merkmal mehrere Verfahren an einem Werkstück
- Möglichkeit der Nachbewertung nach jedem Merkmal
- Erstellung der jeweiligen Formblätter je Verfahren
- Ergebnis der gesamten Untersuchung und Verwendungsentscheid in der Übersicht
- Nach Abschluss der Untersuchung Eintrag in die Prüfmittel-Historie
Die Prüfmittelfähigkeit berücksichtigt:
- Das Messen an Serienteilen
- Die Benutzung durch mehrere Werker
- Prüfstände mit eingebauten Messsystemen
- Umweltbedingungen, wie sie am Arbeitsplatz anzutreffen sind
- Automatische Prüfsysteme
Vorgaben für Fähigkeitsuntersuchungen
- Zum Prüfmitteltyp kann eine Frist für eine wiederkehrende Fähigkeitsuntersuchung angegeben werden. An welchem Prüfmittel dieses Typs dann die Untersuchung ausgeführt wird, entscheidet der Anwender.
- In den Stammdaten des Prüfmittels können Vorgaben in Bezug auf die Durchführung einer Fähigkeitsuntersuchung nach jeder Prüfung gemacht werden. Die Auswahl unterscheidet hier zwischen 'nicht erforderlich', 'Vorschlag' oder 'Durchführung'.
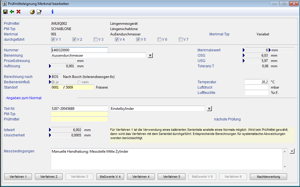
Angaben zum Merkmal
- Werkstück mit Teile-Nr. und Benennung
- Merkmalswert mit Maßeinheit und Toleranzen
- Prozessstreuung (Verfahren 1)
- Auflösung
- Berechnungsverfahren (4s, 6s oder prozessbezogen)
- Messbedingungen in Form von Temperatur, Luftdruck und Feuchte
- Bezugsnormal als Teile-Nr. mit Benennung oder Prüfmittel
- Istwert des Normals mit Unsicherheit
Verfahren 1
Bestimmung der Fähigkeit als Cgm und Cgmk
- Wiederholmessungen in Form von mindestens 50 Werten (mehr sind möglich) mit kalibriertem Normal oder Serienteil
- Messung am Einsatzort
- Angabe des Bedieners
- Messung absolut oder relativ
- Berechnung von Mittelwert, Standardabweichung sowie der Fähigkeitsindizes Cgm, Cgmk
- Verwendungsentscheid aufgrund von Mindestwertvorgaben
- Angabe Entscheider mit Kostenstelle
- Vermerke
Verfahren 2
 Gesamtstreubereich mit mehreren Bedienern
Gesamtstreubereich mit mehreren Bedienern
- Relative oder absolute Messung
- Keine Einschränkung der Anzahl der Bediener (üblich 2)
- Keine Einschränkung der Anzahl der Teile (üblich 10)
- Berechnung Prozentwert des Streubereiches
- Unterstützung der ARM-, Differenzen- und ANVOA-Methode
- Verwendungsentscheid: fähig (0-10%), bedingt fähig (10-30%), nicht fähig (> 30%)
Verfahren 3
Gesamtstreubereich ohne Bediener-Einfluss
- Relative oder absolute Messung
- Keine Einschränkung der Anzahl der Teile (üblich 25)
- Ermittlung Streubereich über alle Messreihen
- Unterstützung der ARM-, Differenzen- und ANVOA-Methode
- Verwendungsentscheid wie bei Verfahren 2
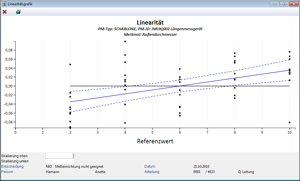
Verfahren 4
Linearitätsbestimmung
- Wichtig für Messbereiche mit Kennlinien
- Variable Anzahl von Stützstellen über Arbeitsbereich
- Prüfung mit Normalen
- Mehrfachmessung je Stützstelle
- Ergebnisdarstellung als Grafik
- Je Stützstelle Einzelwerte, Mittelwert
- Über Messbereich Kurvenverlauf 95%-Messbereich
- Überprüfung Nullpunkte (grün) im Vertrauensbereich
Verfahren 5
- Überwachung Langzeitverhalten während der Nutzung
- Mehrfache Prüfung eines Teiles (Normal)
- Prüfung mit gewöhnlichem Fertigungs-Prüfauftrag parallel zur Fertigungsprüfung
- Alle Informationen zur Messbeständigkeit im Bericht enthalten
Verfahren 6
Qualitative Prüfungen an genau vermessenen Teilen
- Festlegung der Anzahl der Prüfer
- Auswahl Teile aus der Fertigung, so dass der gesamte Toleranzbereich abgedeckt wird
- Genaues Vermessen der Teile zur Ermittlung der Anzahl der Teile außerhalb und innerhalb der Toleranzgrenzen
- Anschließend qualitative Prüfung an jedem Teil und Erfassung, ob innerhalb oder außerhalb der jeweiligen Toleranzgrenze
- Kennwert %GRR abhängig von der Zahl der Übereinstimmungen
- Verwendungsentscheid analog Verfahren 2
Importschnittstelle
- Verfahren 1, 2 und 3 erlauben einen Import über die Q-DAS-Schnittstelle.
Schnittstellen zu anderen Modulen